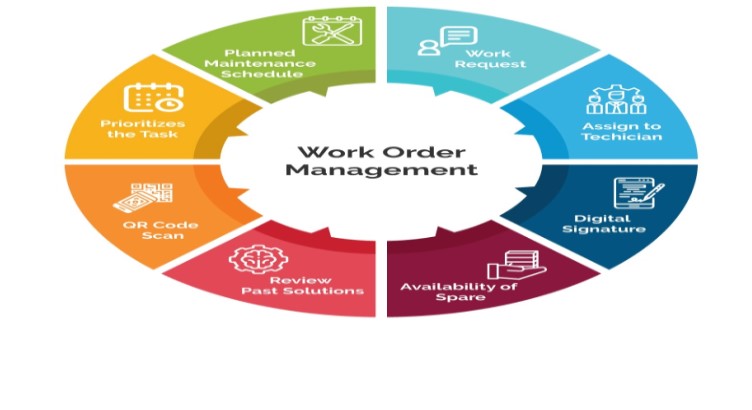
Work Order Management is a systematic approach to creating, assigning, tracking, and completing maintenance and repair tasks within an organization. It is a critical component of facilities management, ensuring that all maintenance activities are carried out efficiently and effectively.
Key Components of Work Order Management:
- Work Order Creation: Initiating a work order based on a maintenance request or scheduled maintenance task.
- Work Order Assignment: Assigning the task to a technician or maintenance team with the appropriate skills and availability.
- Work Order Tracking: Monitoring the progress of the work order from initiation to completion.
- Work Order Completion: Ensuring the task is completed correctly and closing the work order.
- Work Order Reporting: Generating reports on completed work orders for analysis and improvement.
Steps in Work Order Management:
- Request Submission: A maintenance request is submitted by personnel, often through a work order management system.
- Work Order Creation: The maintenance request is converted into a work order, detailing the task, priority, and required resources.
- Task Assignment: The work order is assigned to the appropriate technician or team.
- Work Execution: The technician completes the task, updating the work order with progress and completion details.
- Quality Control: The completed work is inspected to ensure it meets the required standards.
- Closure and Documentation: The work order is closed, and all relevant information is documented for future reference and analysis.
Benefits of Work Order Management:
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlines the maintenance process, reducing downtime and improving response times.
- Enhanced Communication: Facilitates better communication between maintenance teams and other departments.
- Improved Resource Allocation: Ensures that the right personnel and materials are used for each task.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Provides valuable data for analyzing maintenance performance and planning future activities.
- Compliance and Safety: Helps ensure that maintenance activities comply with safety regulations and standards.
Features of Work Order Management Systems:
- Automated Work Order Generation: Automatically generate work orders based on scheduled maintenance or triggered by condition monitoring.
- Mobile Access: Technicians can access and update work orders from mobile devices in the field.
- Real-Time Tracking: Monitor the status of work orders in real time, providing visibility into maintenance activities.
- Integration with Other Systems: Integrate with other enterprise systems, such as inventory management and ERP systems, for seamless operations.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generate reports and analytics to track performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
- Priority and Scheduling: Set priorities and schedules to ensure critical tasks are completed first.
Best Practices in Work Order Management:
- Standardization: Use standardized procedures and templates for creating and managing work orders.
- Prioritization: Prioritize work orders based on urgency, impact, and available resources.
- Communication: Maintain clear and consistent communication among all stakeholders.
- Training: Provide ongoing training for maintenance personnel on the use of the work order management system.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct regular reviews of work order data to identify areas for improvement.
- Preventive Maintenance: Implement preventive maintenance strategies to reduce the frequency of reactive work orders.
Contact EML for a computerized maintenance management system for work order management.