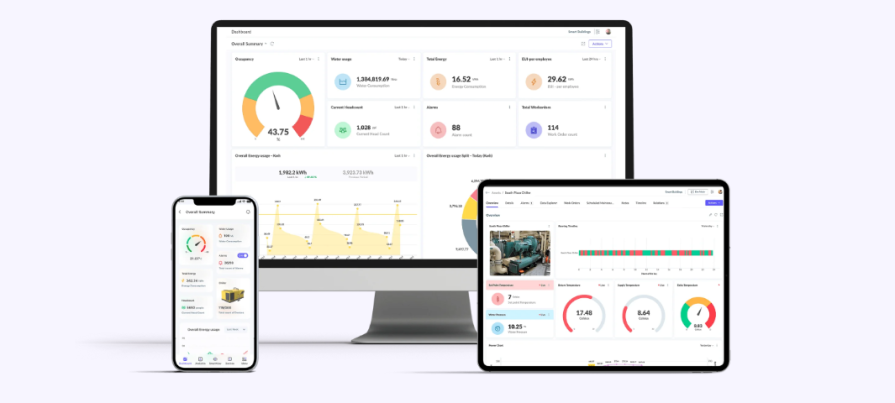
Submetering
Submetering is an effective strategy for detailed energy end use in buildings and facilities. It involves the installation of additional meters (power, water, steam, etc) to monitor energy consumption at a more granular level, such as individual tenants, departments, equipment, or specific areas within a building.
Key Components and Types of Submetering:
-
Electric Meters:
- Measure electricity usage at specific circuits or equipment levels.
- Common in commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and multi-tenant buildings.
-
Water Meters:
- Monitor water usage in different areas or by specific tenants.
- Essential for identifying leaks and promoting water conservation.
-
Gas Meters:
- Track natural gas consumption for heating, cooking, or industrial processes.
- Useful for managing energy costs in facilities with significant gas usage.
-
Thermal Meters:
- Measure the consumption of heating and cooling energy (e.g., steam, hot water, chilled water).
- Common in buildings with central HVAC systems
Benefits:
-
Detailed Submetering:
- Provides precise data on energy consumption for specific areas, tenants, or equipment.
- Helps identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
-
Cost Allocation:
- Enables accurate billing for energy usage in multi-tenant buildings or shared spaces.
- Encourages tenants to be more energy-conscious and responsible.
-
Energy Savings:
- Pinpoints high-energy-use areas or equipment, allowing for targeted energy-saving measures.
- Supports the implementation of energy efficiency projects and tracking of their impact.
-
Enhanced Control:
- Provides building managers with the information needed to optimize energy use.
- Facilitates the proactive management of energy consumption, reducing waste.
-
Regulatory Compliance:
- Helps buildings meet regulatory requirements and energy efficiency standards.
- Supports reporting for energy certification programs (e.g., LEED, ENERGY STAR).
EMLOnline is your solution for online energy submetering. Let us put our experience to use for you.